User account login failed? User account login success ? looks like the user has forgotten his password! Closing the incident as false-positive, Oh bad! stop doing this, We need to get some more insights on the events and understand much more about the user behaviors. Event ID 4625 will represent the user who has failed logins and the same user logged with correct credentials Event ID 4624 is logged.
Dealing with such events will take much dwell time to analyze. Knowing and correlating the right logon types will save you hunt time. In this blog, we will see the mindmap of handling the will know events IDs ( 4625 & 4624 ) which is very normal with legitimate users also.
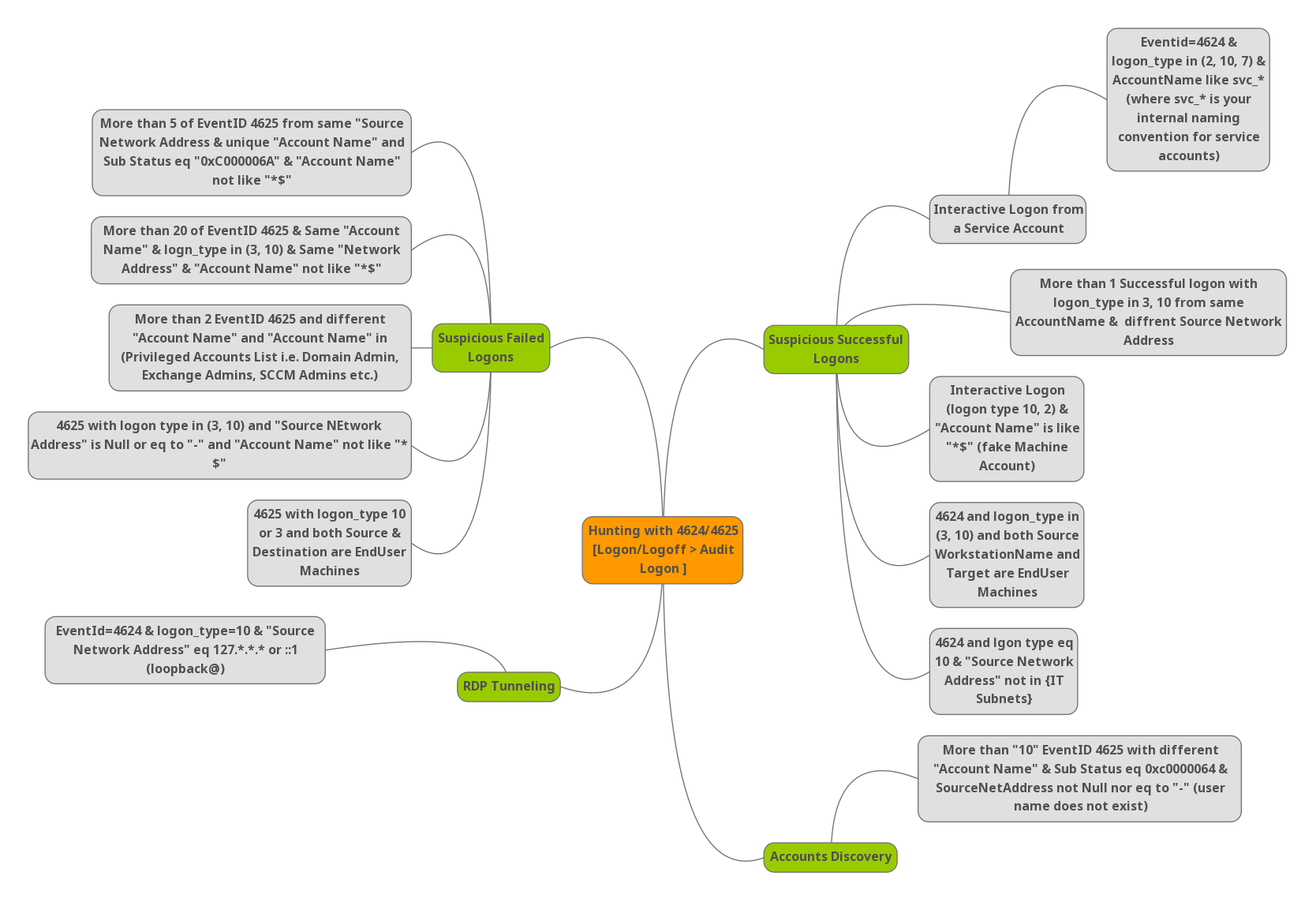
How to avoid those normal users’ noise in logs and hunt only the attacker’s activities. Please find the below cheatsheet.
Also Read : Threat Hunting using Sysmon – Advanced Log Analysis for Windows
Windows Logon Types :
| Logon Type | Logon Title | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Interactive | A user logged on to this computer. |
| 3 | Network | A user or computer logged on to this computer from the network. |
| 4 | Batch | Batch logon type is used by batch servers, where processes may be executing on behalf of a user without their direct intervention. |
| 5 | Service | Service was started by the Service Control Manager. |
| 7 | Unlock | This workstation was unlocked. |
| 8 | NetworkCleartext | A user logged on to this computer from the network. The user’s password was passed to the authentication package in its unhashed form. The built-in authentication packages all hash credentials before sending them across the network. The credentials do not traverse the network in plaintext (also called cleartext). |
| 9 | NewCredentials | A caller cloned its current token and specified new credentials for outbound connections. The new logon session has the same local identity but uses different credentials for other network connections. |
| 10 | RemoteInteractive | A user logged on to this computer remotely using Terminal Services or Remote Desktop. |
| 11 | CachedInteractive | A user logged on to this computer with network credentials that were stored locally on the computer. The domain controller was not contacted to verify the credentials. |
Also Read: Threat Hunting using Firewall Logs – Soc Incident Response Procedure
Suspicious Failed Logons:
- Event ID 4625 is observed for 5 or more times with the sub status 0xC0000064 , Status code ( 0xC000006A ) says user name is correct but the password is wrong and account name not has the value $ , $ says ( Any username that ends with $ is a computer account. ) , In this case we are ignoring the computer account.
- More than 20 events seen for 4625 and the account types are ( 3 & 10 ) and traffic from same network address and account name not has the value $ , In this case our hunting case includes Type 3 ( A user or computer logged on to this computer from the network ) and Type 10 ( A user logged on to this computer remotely using Terminal Services or Remote Desktop )
- More than 2 Events for 4625 and the account names are different and it is privileged account list i.e, Exhange Admin etc.
- Event ID 4625 with logon type ( 3 , 10 ) and source Network address is null or “-” and account name not has the value $
- Event ID 4625 with logon types 3 or 10 , Both source and destination are end users machines.
- More than “10” EventID 4625 with different “Account Name” and Sub status 0xc0000064 , Status code 0xc0000064 says user name does not exist and source network address is not equal to “null” or “-” , Possible accounts discovery.
Also Read: Splunk Architecture: Forwarder, Indexer, And Search Head
Suspicious Successful Logons:
- Event ID 4624 with Logon type 10 ( RemoteInteractive logins ) and source network address is loopback ( 127.*.*.* or ::1 ) , mostly RDP tunneling.
- Event ID 4624 and logon type 10 ( Remote Interactive ) and source network is not in your organization Subnet.
- Event ID 4624 and logon type ( 3, 10 ) and both source work station names and destination are end user machines.
- Event Id 4624 with logon types ( 10 ,2 ) , Type 2 ( A user logged on to this computer ) and account name has ends with $ , Example: ItSupport$ , Possible fake machine account.
- Event Id 4624 with more than 1 successful logon with logon type in 3, 10 from same account name and different source network address.
- Event ID 4624 and logon types ( 2,10,7 ) and account name like svc_* or internal service accounts , Possible interactive logon from a service account.
Happy Hunting!



































