Overview
Microsoft Sigcheck v2.82 is an excellent application that enables you to verify information about files — including digital certificates, version numbers, and timestamp information. , Integration of the popular Virustotal API in Sigcheck could change that dramatically on the other hand. While you still need to run the program from the Windows command prompt, you can now send all files of a folder to Virustotal to return a list of files that at least one of the antivirus engines detected as malicious.
Its dependence on the command prompt is apparently the main reason why it is not used by more major users of the system. One way to use the tool is to check for unsigned files in your windows directories.
Installation steps
- Download Sigcheck v2.82 from https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/sigcheck
- Extract the .zip file.
- Run the .exe file for your system as administrator in command prompt.
- For a 32-bit system, choose sigcheck.
- For a 64-bit system, choose sigcheck64.
Also Read: Latest Ransomware CVEs – Vulnerabilities Abused by Ransomware Actors
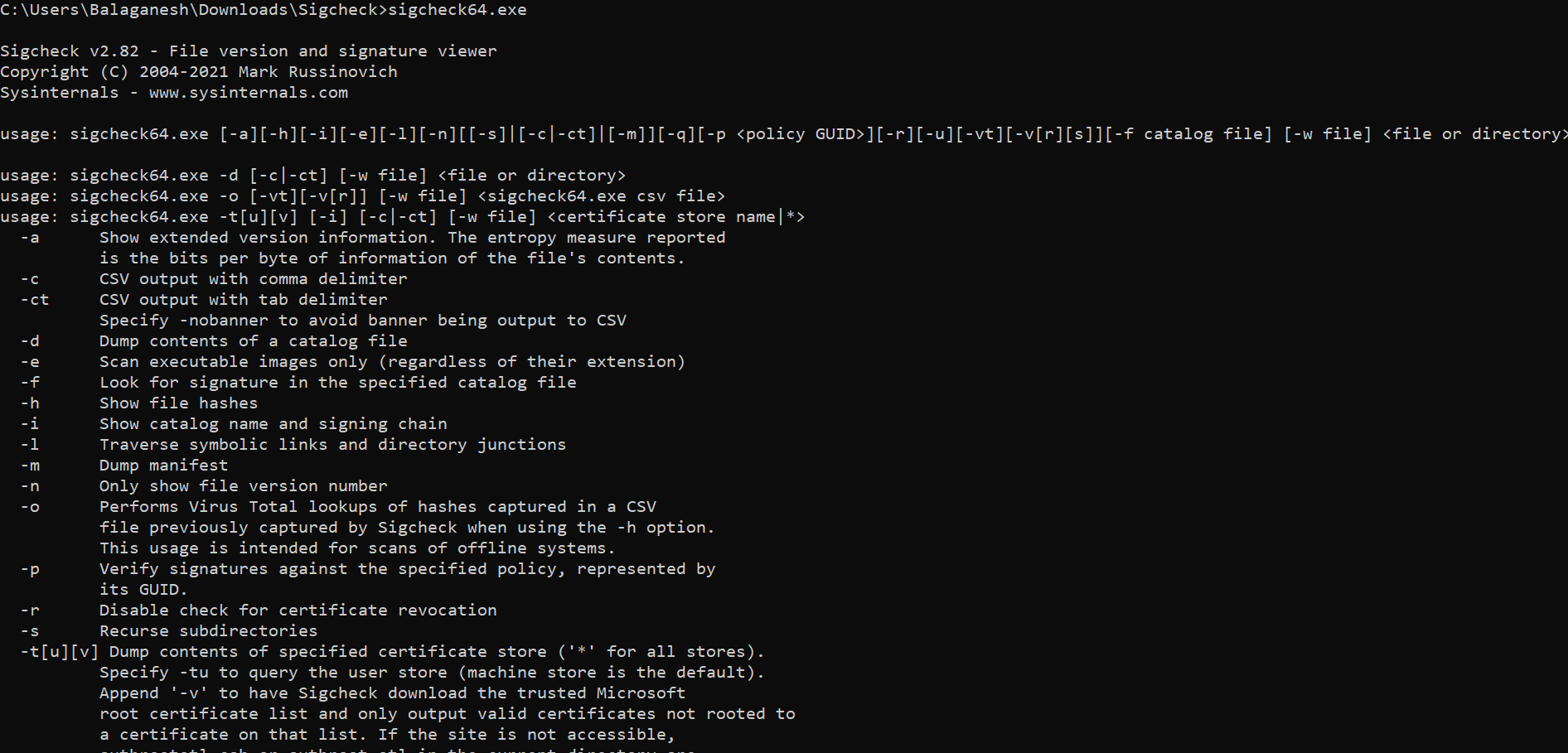
Working with Sigcheck
To do a responsive directory scan, which we upload a list of files to virustotal as automation by sigcheck and provide the detection ratio on the screen.
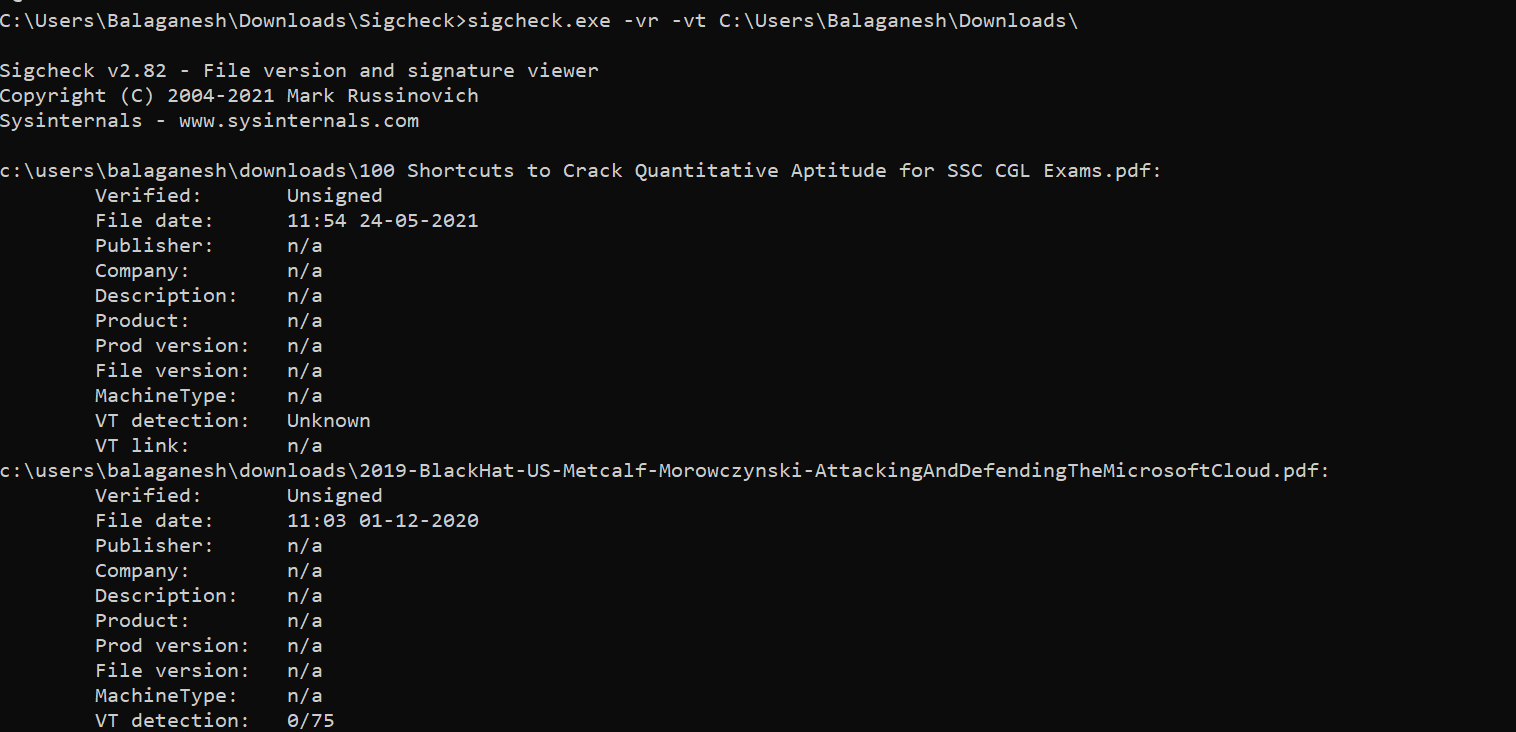
-v [rn] Queries the Virustotal service by using file hashes. The “r” option adds reports for files with non-zero detection, the “n” option prevents the uploading of files that are unknown to Virustotal.
-vt This accepts the terms of service of Virustotal.
The above figure shows All files are uploaded as an automated process and detection is provided faster.
Also Read: Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures – New CVE’s
Scrolling downward and checking all files in the command prompt may be a bit challenging task, so we can ship these results in Microsoft excel as exclusive reports.

–c CSV output with comma delimiter
-e Scan executable images only (regardless of their extension)
-u If VirusTotal check is enabled, show files that are unknown by VirusTotal or have non-zero detection, otherwise, show only unsigned files.
-s Recurse subdirectories
-h Show file hashes
-v Queries the Virustotal service by using file hashes. The “r” option adds reports for files with non-zero detection, the “n” option prevents the uploading of files that are unknown to Virustotal.
Also Read: Cyber Threat Hunting – Proactive Intrusion Detection
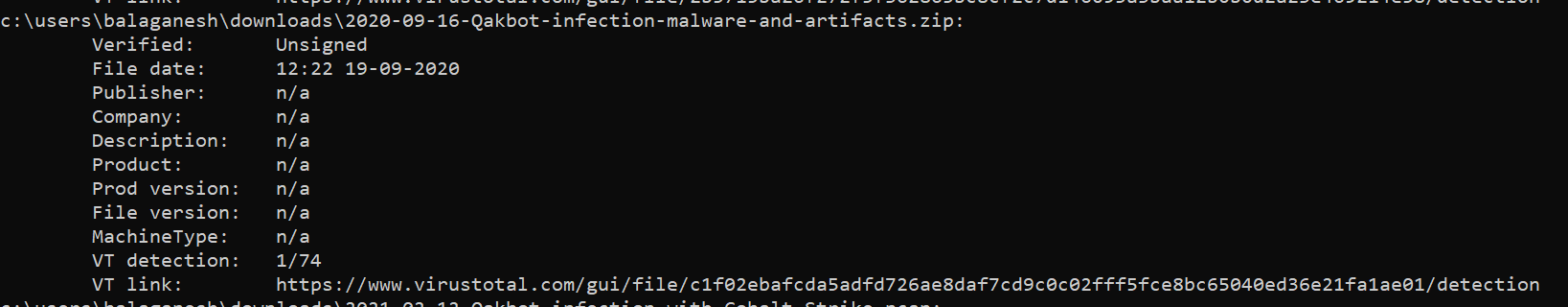
The above query can use to upload files to virustotal and gets the Affected file Path, Signed or unsigned information, Date, Publisher Name, Company, Description, Product, Product Version, File Version, Machine Type, MD5, SHA1, PESHA1, PESHA256, SHA256, IMP, VT detection, VT link.
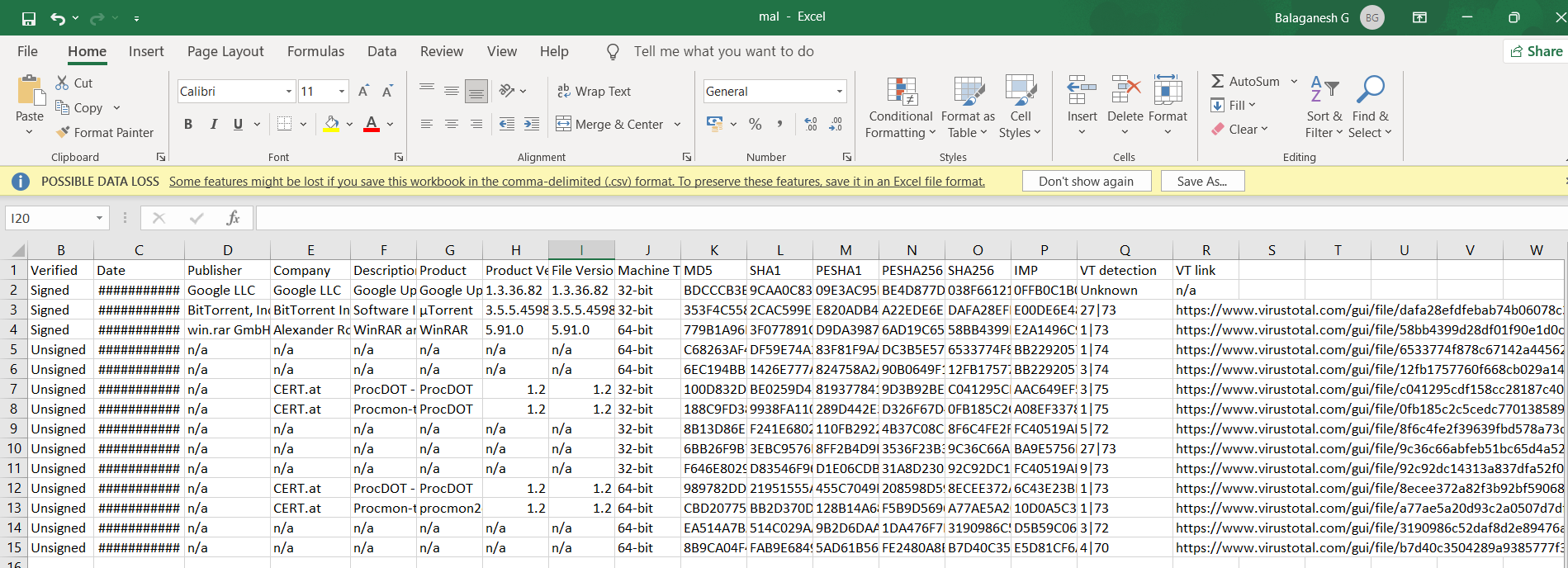
The above illustration shows, the scan was performed and results are exported in CSV for better incident handling. All unsigned files do not mean it is malware, most of the times malware creators uses signed one. So this is a good tool to get essence automated in the mission of incident response to catch offensive stuff.
Also Read: Latest IOCs – Threat Actor URLs , IP’s & Malware Hashes
Conclusion
The tool Sigcheck has been used across by various cybersecurity professionals, especially for incident response and Security operation. The simple tools are more familiar for their robust usage and performance.



































