The Lazarus Group, the North Korean state-sponsored APT, remains one of the most dangerous adversaries. In 2025 their operations have evolved, combining social engineering, supply chain attacks, and malware-laced open source abuse. For SOC teams, staying ahead means understanding their Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures, identifying their malware strains, and deploying strong detection/mitigation controls.
1. Key Lazarus Campaigns in 2025 and SOC Countermeasures
Lazarus’s 2025 tactics blend sophisticated phishing, insider threats, and software tampering, often evading traditional defenses. SOC analysts should focus on mastering threat intelligence, implementing multi-layered verification processes, and leveraging automated tools for anomaly detection to counter these campaigns effectively.
North Korean IT Workers: Infiltrating from Within
One of Lazarus’s most pervasive strategies involves deploying North Korean operatives disguised as remote IT professionals. Since late 2024, these actors have used stolen identities or AI-generated personas to infiltrate U.S. and UK-based tech firms, securing roles that grant access to sensitive networks.
Once inside, they exfiltrate data, install malware, or funnel revenue back to state sponsors. A stark example is the compromise of an Atlanta blockchain company, where insiders siphoned over $900,000 in cryptocurrency, affecting more than 100 U.S. organizations (including Fortune 500 companies).
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Behavioral Monitoring: Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to flag anomalous activities, such as excessive data exfiltration or unauthorized code executions. PyLangGhost RAT is the flagship malware of this campaign: set up alerts for indicators, like suspicious Python processes or connections to known C2 domains.
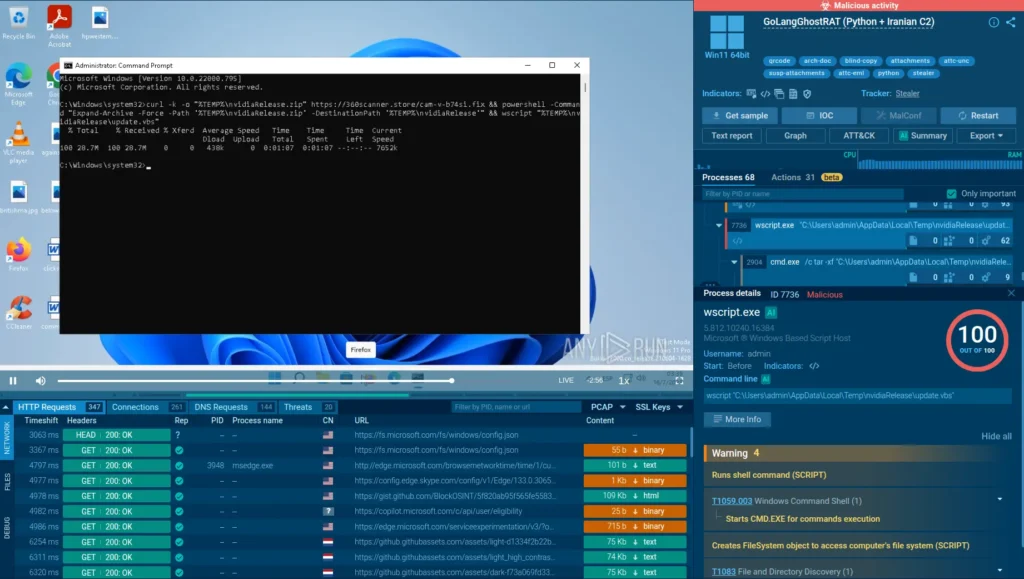
PyLangGhost, malware operated by Lazarus, analyzed in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
- Identity Verification Protocols: Implement rigorous background checks for remote hires, including cross-referencing resumes against public records and using AI-driven identity validation tools. Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all access requests and monitor for unusual IP geolocations (e.g., VPNs masking North Korean origins).
- Protection Strategies: Segment networks to limit lateral movement, conduct regular access reviews, and train HR on red flags like reluctance to video interviews. Use sandbox environments like ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox to test any tools or scripts provided by new hires, reducing insider threat dwell time from weeks to hours.
By integrating these measures, SOC teams can detect infiltrations early, preventing intellectual property theft and regulatory fallout.
| Expose full attack chain in seconds for immediate detection and response Request your trial of ANY.RUN Sandbox |
Operation 99 (Contagious Interview): Social Engineering via Fake Job Offers
Dubbed “Contagious Interview,” Operation 99 targets developers and executives in tech and cryptocurrency sectors. Lazarus operatives masquerade as recruiters on LinkedIn, Telegram, or Calendly, enticing victims with bogus job interviews that deliver malicious coding tests via tainted GitLab repos or NPM packages.
High-level targets receive fake Zoom installers laced with malware, leading to credential theft and system compromises. This has ripple effects, enabling supply chain attacks that infect partners and clients.
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Phishing Awareness and Simulation: Run organization-wide phishing drills focused on recruitment scams, emphasizing verification of sender domains and links. Configure email security gateways to block attachments from untrusted sources and scan for obfuscated JavaScript in interview invites.
- Threat Hunting for Malicious Packages: Monitor developer workflows with tools like dependency scanners to identify tampered open-source code. Hunt for indicators of compromise (IOCs) such as unusual outbound traffic to C2 servers during “interviews.”
- Protection Strategies: Enforce zero-trust access for collaboration tools, requiring device compliance checks before granting session access. Post-incident, isolate affected endpoints and perform full forensic analysis to trace infection vectors, mitigating downstream risks to supply chains.
SOC teams that prioritize user education and automated scanning can disrupt this campaign at the entry point, preserving operational integrity.
Hijacking Open-Source Packages: Supply Chain Sabotage
Lazarus has aggressively compromised open-source ecosystems since September 2024, cloning legitimate GitHub and PyPI repositories to insert backdoors. By early 2025, over 230 malicious packages were detected, impacting 36,000 companies across Europe, India, and Brazil.
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Supply Chain Vigilance: Integrate software bill of materials (SBOM) tracking into CI/CD pipelines to audit package integrity. Use reputation-based blocking in package managers to quarantine suspicious uploads.
- Detection Tactics: Employ network traffic analysis to spot beaconing to Lazarus-associated domains (e.g., those linked to North Korean infrastructure). Scan for behavioral anomalies like unexpected privilege escalations in development environments.
- Protection Strategies: Adopt air-gapped testing for third-party code and enforce code signing requirements.
These steps empower SOC analysts to fortify the software supply chain, averting widespread compromises.
2. Current Lazarus Malware Threats: Detecting and Mitigating
Lazarus’s malware arsenal in 2025 is modular and evasive, designed for stealthy persistence and data exfiltration. SOC analysts should leverage interactive sandboxes, SIEM integrations, and YARA rules for rapid identification.
InvisibleFerret: Stealthy Data Harvester
This modular implant, often spread through fake interview lures, excels at keylogging, screenshot capture, and C2 communication. It targets developer machines to siphon code and credentials, blending into legitimate processes to evade antivirus.
View a sandbox analysis of InvisibleFerret sample
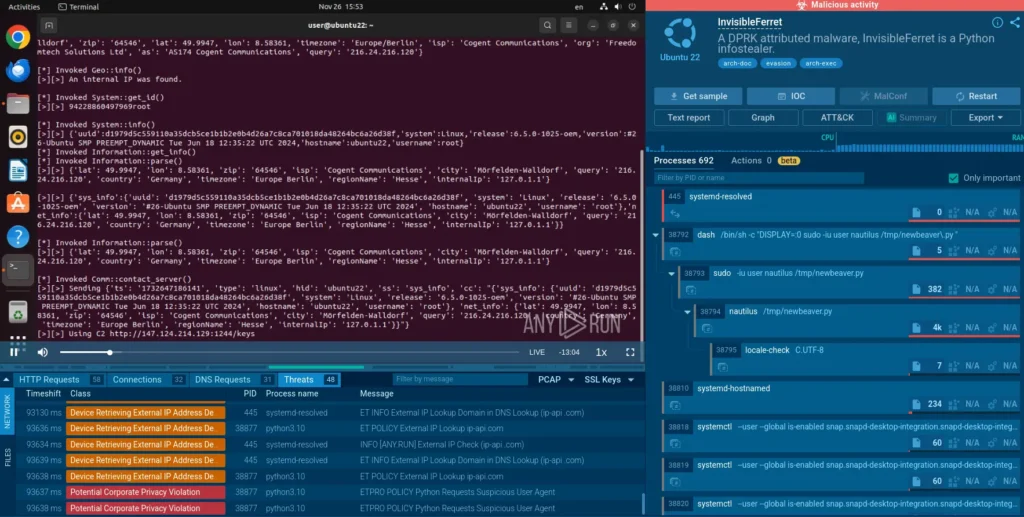
InvisibleFerret detonated in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Detection Methods: Use behavioral analytics in EDR tools to detect processes spawning unusual child activities (e.g., keyloggers hooking into input streams). Monitor for connections to non-standard ports (e.g., 443/TCP mimicking HTTPS but routing to C2). Deploy YARA signatures for its modular DLLs and scan sandboxed samples for verification.
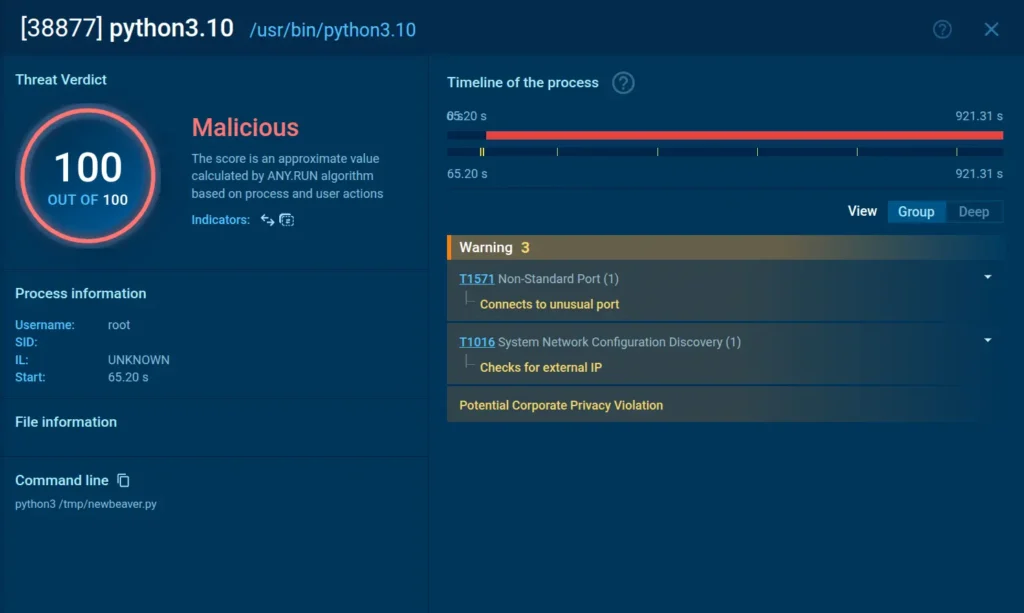
Malware connects to an unusual port as seen in Interactive Sandbox
- Protection Strategies: Harden endpoints with application whitelisting and restrict PowerShell/CLI usage in dev environments. Upon detection, isolate the host, revoke stolen credentials via privileged access management (PAM), and conduct threat hunting across the network to uncover lateral movement.
| Boost your SOC performance: detections up, MTTR down Try ANY.RUN Sandbox with interactivity and anti-evasion: request trial |
PyLangGhost: Python-Based Ghost in the Machine
Associated with IT worker infiltrations, PyLangGhost masquerades as benign Python scripts to establish persistence and exfiltrate data. It leverages legitimate libraries for obfuscation, targeting blockchain and financial apps.
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Detection Methods: Configure SIEM rules for anomalous Python executions (e.g., high-volume network calls from python.exe). Analyze file hashes against known IOCs and use memory forensics to uncover injected code. Sandbox suspicious scripts to observe behaviors like dynamic imports.
View a sandbox analysis of PyLangGhost RAT
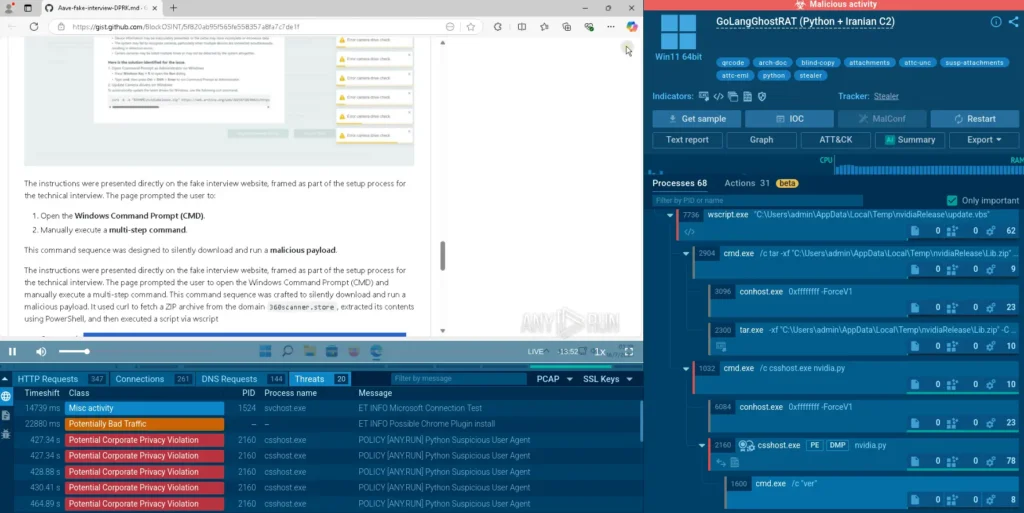
ANY.RUN’s Interactivity feature allows to emulate user actions needed to detonate the malware
- Protection Strategies: Limit Python runtime environments with containerization (e.g., Docker with seccomp profiles) and monitor for privilege abuse. Educate teams on safe scripting practices and integrate API-based monitoring for cloud services to block unauthorized exfiltration.
OtterCookie: Cross-Platform Credential and Crypto Stealer
Emerging in late 2024 and rapidly evolving through 2025, OtterCookie is a modular stealer malware linked to Lazarus’s Contagious Interview campaign, targeting finance and tech professionals via fake job offers and deepfake videos.
Written in heavily obfuscated JavaScript or .NET, it extracts browser credentials (e.g., Chrome, MetaMask), macOS Keychain passwords, digital certificates, crypto wallet private keys, keystrokes, and files. Delivered through tainted coding challenges, video software, or npm packages, it enables espionage and financial theft in crypto sectors.
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Detection Methods: Scan for obfuscated JavaScript in developer tools or email attachments using deobfuscators like Deobfuscator.io, and monitor for VM evasion attempts via process analysis. Integrate EDR alerts for unusual browser interactions, keylogging hooks, or exfiltration to Lazarus C2 domains. Use sandbox environments to detonate samples and extract IOCs like file hashes or network beacons.
Thanks to the analysis inside ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, we can observe the entire attack chain for this malware.
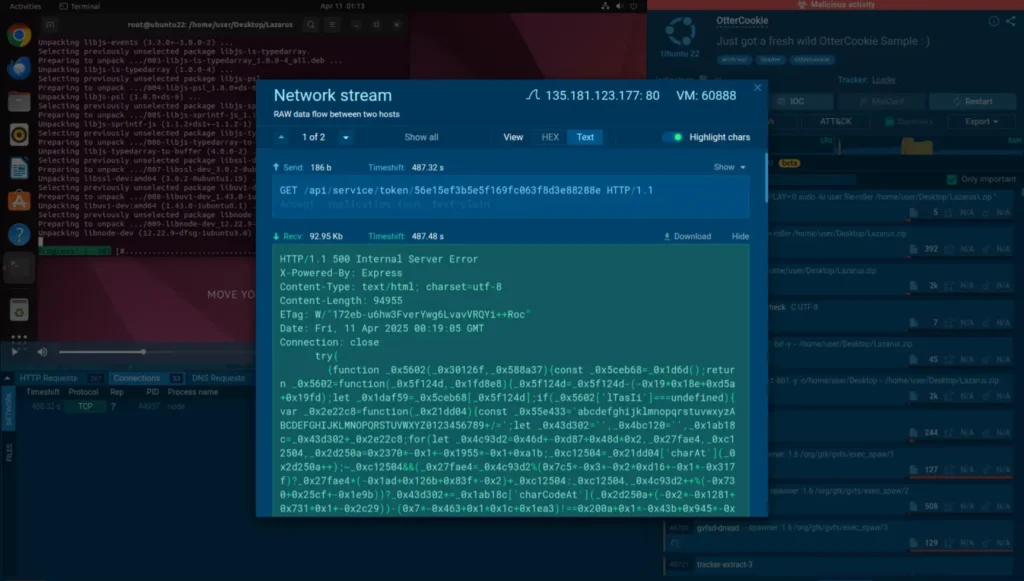
OtterCookie gets payload from an external server
- Protection Strategies: Enforce script execution policies (e.g., PowerShell Constrained Language Mode) and browser sandboxing to limit credential access. For crypto environments, isolate wallet apps with hardware security modules (HSMs) and monitor for anomalous API calls to exchanges. Train users on verifying job offers with video deepfake detection tools, and implement automated dependency scanning in CI/CD to block tainted packages.
Additional Malware Families: BLINDINGCAN, FASTCASH, and Variants
Lazarus deploys BLINDINGCAN for Android/iOS spying in supply chain hits and FASTCASH for ATM/cryptocurrency heists. These evolve with anti-analysis tricks, like VM detection evasion.
Recommendations for SOC Analysts:
- Detection Methods: For mobile threats, scan app stores and sideloaded APKs with VirusTotal or custom rules. Track FASTCASH via unusual SWIFT message patterns in financial logs. Use ML-based anomaly detection for evolving TTPs.
- Protection Strategies: Implement mobile device management (MDM) with app vetting, and segment financial systems with air-gapping. Regularly update firmware and conduct red-team exercises simulating Lazarus TTPs to test defenses.
Building Organizational Resilience Against Lazarus: How ANY.RUN’s Solutions Help
To protect against Lazarus in 2025, SOC analysts must adopt a defense-in-depth approach that combines enhanced threat intelligence, incident response optimization and proactive measures like vulnerability assessments and backing up critical data offsite.
- Utilize ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox to upload and detonate suspicious files or links in a safe environment, enabling real-time interaction (e.g., typing, scrolling) to analyze malware behaviors, extract IOCs, and decrypt configs for threats like InvisibleFerret, PyLangGhost, and OtterCookie.
- Employ Threat Intelligence Lookup to query shared data from thousands of investigations, speeding up IOC identification and contextual analysis of Lazarus TTPs, such as those in social engineering campaigns.
- Integrate TI Feeds via API or STIX/MISP into SIEM, TIP, or XDR systems for real-time anomaly detection, enriching defenses with fresh IOAs and IOBs from global experts to counter supply chain attacks and APTs, ultimately reducing mean time to respond (MTTR) and boosting detection rates.
Defending against Lazarus Group attacks requires a comprehensive approach combining technical controls, employee awareness, and robust incident response capabilities. SOC analysts must remain vigilant for the evolving tactics of this persistent threat actor while implementing layered defenses that address both technical vulnerabilities and human factors in the attack chain.
Regular review and updates of these procedures are essential as Lazarus continues to adapt its methods. Organizations should maintain strong threat intelligence capabilities and participate in information sharing to stay ahead of emerging attack techniques and indicators of compromise.



































